Over the past few years, there has been a growing demand for lactose-free milk, as more and more people are choosing to eliminate dairy from their diets. Lactose-free milk is a dairy product that has had the lactose removed, making it easier to digest for those who are lactose intolerant. In this blog, we will explore the reasons why there is a growing demand for lactose-free milk.
Lactose intolerance is a condition where the body is unable to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. People who are lactose intolerant may experience symptoms such as bloating, gas, abdominal pain, and diarrhea after consuming dairy products. It is estimated that up to 75% of the world’s population may be lactose intolerant to some degree.
Health Benefits
One of the main reasons for the growing demand for lactose-free milk is the health benefits it provides. Regular milk contains lactose, which is a complex sugar that is difficult for some people to digest. When lactose is not properly broken down in the small intestine, it can lead to the symptoms of lactose intolerance.
Lactose-free milk is a dairy product that has had the lactose removed. It contains the same nutrients as regular milk, including calcium, vitamin D, and protein, but without the lactose. This makes it a great alternative for people who are lactose intolerant but still want to enjoy the taste and benefits of milk.
Calcium is an essential nutrient that is needed for strong bones and teeth. The body needs vitamin D in order to absorb calcium. Milk is a rich source of both calcium and vitamin D. Lactose-free milk provides the same nutrients as regular milk, making it a great alternative for people who are lactose intolerant.
Digestive Issues
Another reason for the growing demand for lactose-free milk is digestive issues. People who are lactose intolerant may experience uncomfortable digestive symptoms after consuming dairy products. These symptoms may include bloating, gas, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
By choosing lactose-free milk, people can avoid these symptoms and still enjoy the taste and benefits of milk. Lactose-free milk is easier to digest than regular milk, which makes it a great alternative for people who have digestive issues.
Convenience
Lactose-free milk is also a convenient alternative for people who want to avoid dairy but still enjoy milk in their diet. It can be used in cooking and baking, as well as for drinking and making smoothies. Lactose-free milk can be substituted for regular milk in any recipe.
For people who are lactose intolerant, finding alternatives to dairy products can be a challenge. Lactose-free milk provides a convenient and delicious alternative that can be easily incorporated into a variety of recipes.
Increasing Availability
The availability of lactose-free milk has also increased in recent years, with many supermarkets and health food stores stocking a variety of brands and flavors. This has made it easier for people to find and purchase lactose-free milk.
Many dairy companies have recognized the growing demand for lactose-free milk and have started producing their own brands. This has led to a greater variety of lactose-free milk products on the market.
Environmental Concerns
Finally, some people may choose lactose-free milk for environmental reasons. Dairy farming can have a significant impact on the environment, including greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and land use. By choosing lactose-free milk, people may be making a more sustainable choice for the planet.
Lactose-free milk is still a dairy product and has some impact on the environment. However, by choosing lactose-free milk, people may be reducing their environmental impact compared to consuming regular milk.
Also Read: Choose The Milk That Suits You

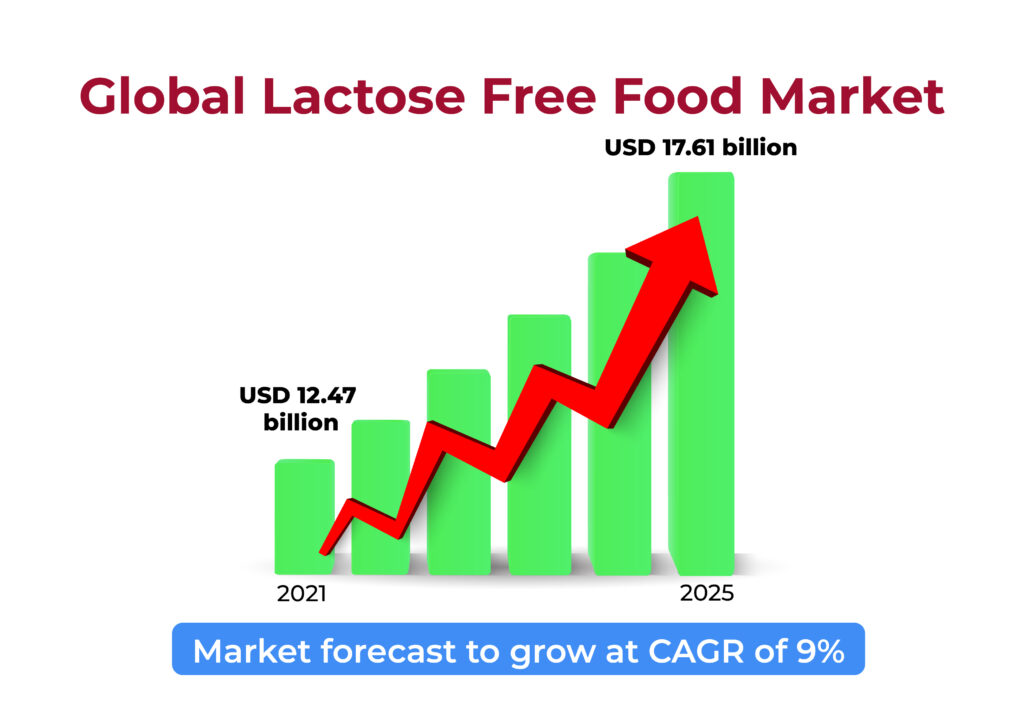
Future Prospects for the Lactose-Free Milk Market
In grownups, lactose intolerance affects anywhere between 65 and 90 percent of people, according to the National Library of Medicine. While the percentage ranges from 5 to 15% in Europe to 80–90% in Asia, lactose intolerance affects the populations in these regions differently. This demonstrates that there is a sizable market that businesses selling lactose-free goods can capitalize on.
The dairy and food industries now have a wealth of growth potential because of the rise in lactose-free dairy product innovations and customer preferences for nutritious foods and drinks. Contact Active Moo Farms to learn more if you’re interested in our lactose-free milk.
The Verdict
In conclusion, the growing demand for lactose-free milk in India can be attributed to a variety of factors, including health benefits, digestive issues, convenience, increasing availability, and environmental concerns. With up to 75% of the world’s population estimated to be lactose intolerant to some degree, lactose-free milk has become a popular alternative to regular milk.
As a result, the dairy industry has had to adapt to this trend, with some farms producing lactose-free milk and others diversifying into plant-based alternatives to milk. With the continued growth of the lactose-free milk market, it will be interesting to see how the dairy industry continues to respond to changing consumer preferences and demands.
FAQs
Why does milk without lactose last so much longer?
Milk that doesn’t contain lactose is pasteurised at a higher temperature. When opposed to conventional pasteurised milk, which still contains some bacteria, the ultra-pasteurization procedure, which is aimed to completely remove the bacterium content, gives lactose-free milk a refrigerated shelf-life of 60–90 days.
Is dairy milk healthier than lactose-free milk?
Compared to their lactose-free counterparts, dairy-free goods frequently have lower levels of calcium, protein, and/or calories. Also, if you have other allergies, being dairy-free is not the best option (like nuts, soy or seeds).
Does lactose-free milk create a change?
Some people believe lactose-free milk tastes sweeter than ordinary milk when the lactose is converted into simpler sugars. The same vital components, including calcium, protein, vitamin D, and B vitamins, are still present in lactose-free milk aside from that.
Who made lactose-free milk successful?
In order to digest lactose, Cornell University alumnus and owner of a family dairy, Alan E. Kligerman, invented Lactaid. Virginia Harris Holsinger, a chemist with the USD Agricultural research service, was his collaborator. By working together, they introduced lactose-free milk to the market in the middle of the 1980s.




